Understanding the Benefits of Botox Treatments
Botox is a purified neurotoxin that is used in carefully calculated amounts for cosmetic procedures to produce targeted muscle relaxation. Effects generally appear within days and resolve as normal signaling returns. Qualified medical professionals administer it using defined techniques to meet specific treatment goals.
What Is Botox?
Botox is injected directly into designated muscles, where its medical action involves temporarily halting muscle contraction in the treated area. This localized effect causes muscle relaxation that is not permanent, as normal nerve function and muscle activity return gradually over several months. Dosing and injection sites are determined based on patient needs and clinical judgement. The process requires medical expertise to achieve intended muscle relaxation, aiming to reduce side effects. Regular assessment and reevaluation guide the frequency of repeat treatments.
Who Does It Benefit?
The procedure appeals to a diverse range of adults wishing to enhance a smoother, more relaxed facial expression. Botox addresses dynamic facial wrinkles, which are creases formed by muscle movement. Botox relaxes the underlying muscles in these areas, leading to smoother skin. Common treatment areas include:
- Glabellar lines (frown lines between the eyebrows)
- Forehead wrinkles
- Crow’s feet (lines at the outer corners of the eyes)
Treatments are temporary, so periodic follow-up injections may be needed to maintain visible effects. Candidates for medical Botox treatments receive a specific diagnosis and care plan from a physician. Indications and dosing are determined by a careful evaluation of symptoms and treatment response.
What Does It Involve?
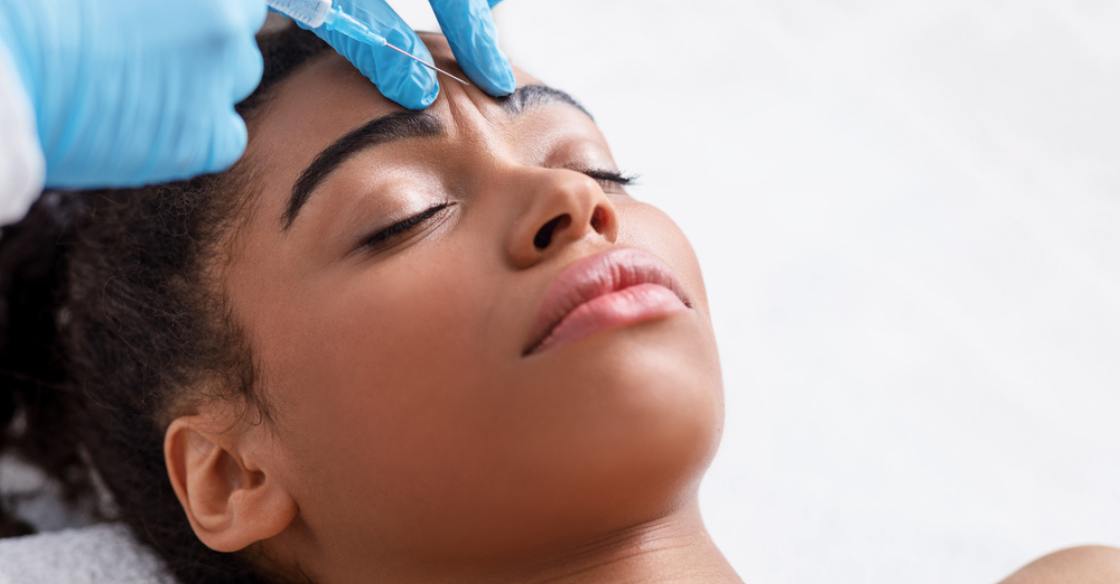
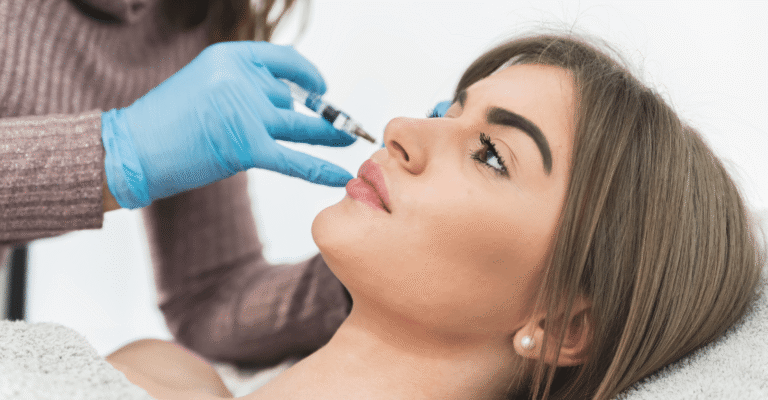
All Botox treatments start with a medical consultation. The healthcare provider reviews one’s medical history to determine whether the procedure is suitable. Certain neuromuscular disorders or active infection at the proposed injection site are checked to promote patient safety. The procedure is performed in a medical office, where a provider cleans the treatment area and injects small, precise amounts of Botox using a fine needle. Pain at the injection site is typically mild. For those with sensitivity, a topical numbing agent or ice may be applied beforehand.
The quantity and distribution of injections depend on the indication. Cosmetic procedures usually involve multiple small doses across the target area, while medical uses require placement based on symptom patterns and muscle group activity. Normal activities are generally resumed right after treatment, but providers may advise patients to remain upright for several hours post-injection. Mild and temporary side effects, such as swelling, bruising, pain, or redness at the injection site, may occur. Repeat procedures are guided by the duration of effect and clinical response and can range from every three to six months or as needed.
Consult a Medical Expert
Any decision to receive Botox for cosmetic indications should be discussed with a medical expert. Botox should only be administered by qualified healthcare professionals who can assess patient suitability and provide individualized care. A focused consultation typically includes a review of personal health history, ongoing medical conditions, and anticipated outcomes, leading to safer and more effective treatments. Regular follow-up and clear communication with your provider help optimize results and address any concerns during your course of care.