Types of Arthritis and Available Treatments
Arthritis remains one of the most common health conditions affecting adults. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis and related conditions. While it occurs more frequently as people age, it is not an inevitable part of getting older. Understanding the nuances of this condition helps individuals recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate care.
What Is Arthritis?
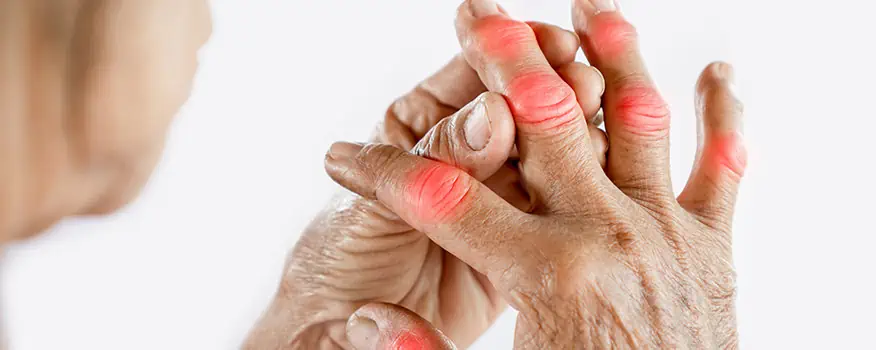
Arthritis is generally characterized by swelling and tenderness of one or more of your joints. The main symptoms are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. Because there are so many variations of the condition, medical professionals often categorize them into broader groups to better manage treatment.
Degenerative Arthritis
The most common type is osteoarthritis. This condition occurs when the flexible tissue at the ends of bones wears down. The wearing down of protective tissue occurs gradually and worsens over time. When the cartilage wears away, bone rubs against bone, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Inflammatory Arthritis
A healthy immune system generates internal inflammation to get rid of infection and prevent disease. But with inflammatory arthritis, the immune system goes awry, mistakenly attacking the joints with uncontrolled inflammation, potentially causing joint erosion. Rheumatoid arthritis often affects the smaller joints first. Psoriatic arthritis affects some people who have psoriasis, a condition that features red patches of skin topped with scales.
How Does It Impact Life?
Living with arthritis means navigating physical challenges that can vary from day to day. The most immediate impact is usually pain. This pain may range from a dull ache to a sharp, burning sensation. Along with pain comes stiffness, potentially most notable in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
These physical symptoms can translate into functional limitations, as simple tasks that many take for granted become difficult. This loss of mobility may affect a person’s ability to work or participate in social activities. Chronic pain can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue that compounds the difficulty of managing the condition during waking hours.
How Is It Treated?
While there is currently no cure for most types of arthritis, a wide range of treatments exists to slow the progression of the disease and manage symptoms effectively. The goal of treatment is to reduce pain and improve function. Weight management is a primary strategy. Losing excess weight reduces the stress on weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees. Regular physical activity is beneficial. Low-impact exercises keep joints flexible and may strengthen the muscles that support them.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are frequently used to reduce pain and inflammation. For more persistent cases, doctors may recommend injections. Viscosupplementation involves injecting a fluid into the joint to improve lubrication and movement.
Physical therapy focuses on exercises that improve the joint’s range of motion and strengthen the muscles surrounding it. In cases where conservative measures no longer provide relief and joint damage is severe, surgical options are available. Joint replacement can dramatically restore a joint’s functionality and motion.
Speak With an Orthopedic Specialist
Managing joint health is a long-term process that requires expert guidance. An orthopedic specialist can provide a precise diagnosis and develop a tailored treatment plan, addressing your specific type of arthritis and lifestyle needs. Early intervention is key to managing symptoms. If you experience persistent joint discomfort, seek professional advice to explore the full range of therapeutic options available to you.