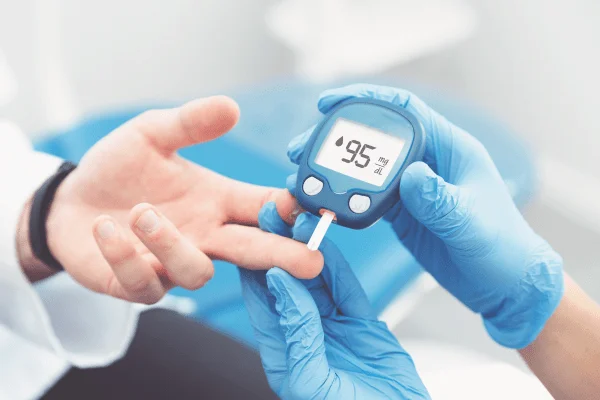
Tips for Diabetes Management
Diabetes is a condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. Most of the food you eat is broken down into sugar, also called glucose, and released into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. With diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use the insulin it makes as well as it should. There isn’t a cure for diabetes, but you can manage the condition and live a healthy life. Learning about diabetes and how to manage it is a step toward promoting wellness.
Food and Exercise
What you eat directly impacts your blood sugar, and a balanced diet is fundamental to diabetes management. Focus on eating a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Portion control is also recommended for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Reading food labels can help you understand what is in your food, so you can make informed choices about carbohydrates and sugars.
Physical activity is another key part of managing diabetes. Exercise helps lower your blood glucose levels by making your body more sensitive to insulin. Aim for regular activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling; even small amounts of movement throughout the day can make a difference. Before starting any new exercise routine, discuss your plans with a healthcare provider to verify it is appropriate for your individual health situation.
Medicine and Alcohol
For many people with diabetes, diet and exercise are not enough to control blood sugar levels, and medication is a necessary component of their management plan. There are several types of diabetes medications, including oral pills and injectable insulin. It is recommended that you take your medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor, and do not skip doses or change your medication schedule without medical guidance. Consistency helps maintain stable blood sugar and prevents complications.
Alcohol consumption can also affect blood sugar. Alcoholic beverages can cause blood sugar to either rise or fall, depending on the type of drink and whether you have eaten. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation. It is often recommended to have alcohol with a meal to avoid low blood sugar. Monitor your blood glucose levels carefully if you drink alcohol, and be aware of how it affects you personally.
Stress and Illness
When you are stressed, your body releases hormones that can raise your blood sugar. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress is a part of your diabetes care plan, and techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or engaging in a hobby can help manage stress. Recognizing your stress triggers is the first step toward effectively addressing them. If you are sick, your body is under stress, which can also raise your blood sugar. You may need to check your blood sugar more frequently when you are ill. Continue taking your diabetes medication, even if you are not eating as much as usual. Have a sick-day plan in place that includes what to eat, how often to check your blood sugar, and when to contact your healthcare provider.
Ask About Diabetes Management Today
Managing diabetes is a daily commitment that involves a combination of lifestyle choices and medical care. Creating a plan that incorporates a balanced diet, regular physical activity, proper medication use, and stress management is advisable. Each person’s needs are different, so your plan should be tailored to you. Working closely with a healthcare team can provide you with the support and information needed to manage your diabetes effectively. Discuss your goals and challenges with your doctor to create a comprehensive management strategy.