Best Treatment Options for Joint Pain in Knees: A Complete Guide
Knee joint pain is a common problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It can interfere with daily activities, limit mobility, and reduce the overall quality of life. Whether caused by aging, injury, or medical conditions like arthritis, knee pain demands proper attention and care. The good news is that there are many effective treatment options available today to help relieve pain, improve function, and get you moving comfortably again.
In this article, we’ll explore the best treatment options for joint pain in knees — from simple home remedies to advanced medical treatments. Our goal is to help you understand what works, what to expect, and how to make the best choices for your knee health.
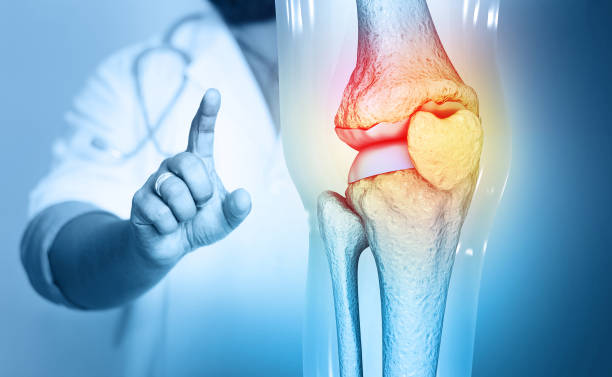
What Causes Knee Joint Pain?
Before diving into treatment options, it’s helpful to understand the common causes of knee joint pain. Knowing the cause can guide the right treatment approach.
- Osteoarthritis: The most common cause, osteoarthritis happens when the cartilage that cushions your knee joint wears down over time, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Injuries: Ligament tears, meniscus injuries, or fractures can cause sudden or chronic knee pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune condition causing inflammation in the knee joint.
- Tendinitis and bursitis: Inflammation of tendons or bursae (fluid-filled sacs) around the knee.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress from activities like running or jumping.
Best Treatment Options for Knee Joint Pain
Treatment depends on the severity of pain, cause, age, and overall health. Here are the top options you can consider:
1. Lifestyle Changes and Home Care
Often, the first step in treating knee pain is making lifestyle adjustments and using simple home remedies.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoid activities that worsen pain. Resting gives your knee time to heal.
- Cold and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs can reduce swelling and numb pain. Heat packs help relax muscles and improve blood flow.
- Weight Management: Extra body weight puts more pressure on knees. Losing weight reduces stress on the joint and often lessens pain.
- Exercise and Stretching: Gentle strengthening exercises improve muscle support around the knee, which helps stabilize the joint and reduce pain. Low-impact activities like swimming and cycling are excellent choices.
- Supportive Devices: Knee braces or shoe inserts can help improve alignment and reduce pain during movement.
2. Over-the-Counter Medications
Pain relief can be achieved through non-prescription medicines:
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) like ibuprofen or naproxen help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Acetaminophen can reduce pain but does not reduce inflammation.
- Always follow dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional if you have other medical conditions.
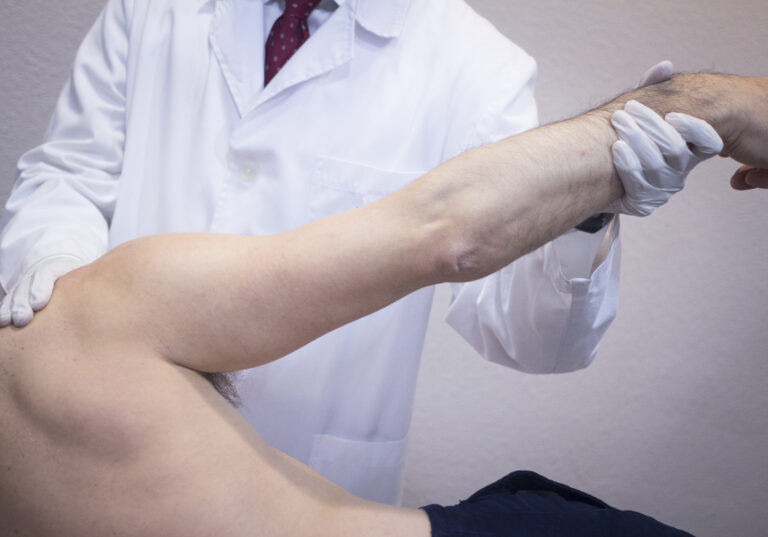
3. Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise plan that:
- Strengthens muscles around the knee
- Improves flexibility
- Restores range of motion
- Teaches proper movement techniques to avoid further injury
Physical therapy is often very effective, especially for osteoarthritis or after an injury.
4. Prescription Medications and Injections
If over-the-counter medications don’t provide enough relief, doctors may prescribe stronger medications or recommend injections.
- Corticosteroid injections reduce inflammation directly inside the knee joint and provide temporary pain relief.
- Hyaluronic acid injections lubricate the joint, improving movement and reducing pain.
- Topical creams or gels can also be prescribed for localized pain relief.
5. Alternative Therapies
Many people benefit from complementary treatments such as:
- Acupuncture: Inserting thin needles at specific points can reduce pain and improve knee function.
- Supplements: Glucosamine and chondroitin are popular supplements that some studies suggest may help joint health, though evidence is mixed.
- Massage therapy: Helps relax muscles and improve circulation around the knee.
6. Surgical Options
Surgery is usually considered only when conservative treatments fail or if the damage is severe.
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to repair or clean out damaged cartilage or ligaments.
- Partial or Total Knee Replacement: In cases of severe osteoarthritis or joint damage, replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial one can relieve pain and restore function.
Tips for Managing Knee Pain Daily
Living with knee pain can be challenging, but these tips may help you manage it better:
- Wear comfortable, supportive shoes.
- Avoid high-impact activities if they cause pain.
- Use a cane or walking aid if needed for extra support.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
- Stay consistent with your exercise routine.
- Listen to your body — don’t push through severe pain.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical help if:
- Knee pain is severe or persistent for more than a few days.
- There is swelling, redness, or warmth around the knee.
- You cannot put weight on your knee.
- The knee locks or feels unstable.
- Pain is accompanied by fever or sudden injury.
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent worsening damage and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Knee joint pain is a common but manageable condition. The best treatment option varies for each person depending on the cause and severity of pain. Most people benefit from a combination of lifestyle changes, exercises, medication, and professional care. In severe cases, injections or surgery may be necessary.
If you’re dealing with knee pain, start with gentle care and consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. With the right approach, you can reduce pain, improve mobility, and enjoy life with healthier knees.
FAQs about Best Treatment Options for Joint Pain in Knees
Q1: Can knee pain go away on its own?
A: Mild knee pain from overuse or minor injury often improves with rest and home care. However, persistent or severe pain should be evaluated by a doctor.
Q2: Are knee braces helpful for joint pain?
A: Yes, knee braces can provide support, improve alignment, and reduce pain, especially during activities.
Q3: Is surgery the only option for severe knee arthritis?
A: Surgery is a last resort. Many people manage severe arthritis with medication, injections, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes before considering surgery.
Q4: What exercises are best for knee pain?
A: Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and specific strengthening and stretching exercises prescribed by a physical therapist are best.
Q5: Are supplements like glucosamine effective for knee joint pain?
A: Some people find relief with supplements, but scientific evidence is mixed. Always consult your doctor before starting any supplement.