Understanding the Risk Factors of Heart Disease: How to Protect Your Heart
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. While many people understand that heart disease is serious, they may not fully grasp the risk factors involved or how they can protect their heart from potential damage. The good news is that most heart disease risk factors are preventable or manageable with lifestyle changes, early intervention, and consistent care. Understanding the key risk factors of heart disease is the first step toward protecting your heart for the long haul.
What is Heart Disease?
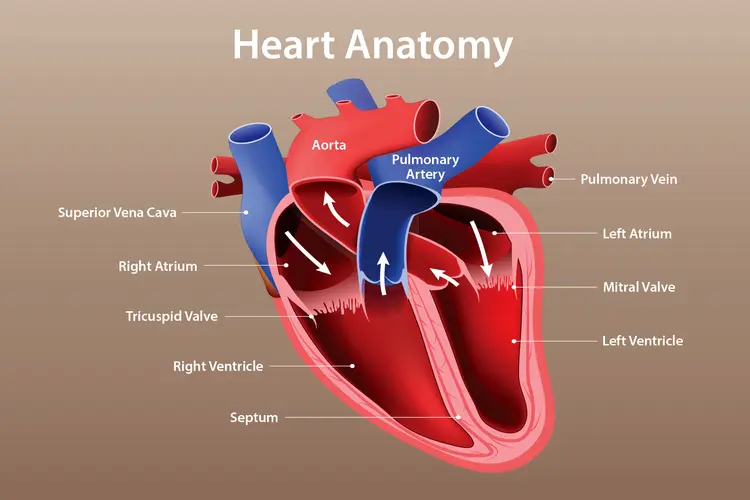
Heart disease refers to a variety of conditions that affect the heart’s structure and function. These conditions include coronary artery disease, heart attacks, heart failure, and arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). The most common cause of heart disease is the build-up of plaque in the arteries, which restricts blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to potentially fatal complications like heart attacks.
Major Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Many factors can increase your risk of developing heart disease, some of which you can control, while others are beyond your control. Below are the most significant risk factors:
1. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
High blood pressure is one of the primary risk factors for heart disease. When blood pressure is consistently high, it can damage the arteries and make the heart work harder. Over time, this can lead to coronary artery disease, heart failure, or even heart attacks. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is crucial, and lifestyle changes such as reducing sodium intake, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help control it.
2. High Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that can build up in the blood vessels, forming plaque that narrows and hardens the arteries. This condition is known as atherosclerosis and can impede blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise cholesterol levels. However, a heart-healthy diet low in these fats, along with regular physical activity, can help lower cholesterol levels.
3. Smoking
Smoking is one of the most harmful habits for your heart. It damages the blood vessels, raises blood pressure, and reduces oxygen flow to the heart, making the heart work harder. Smokers are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, particularly when combined with other factors like high cholesterol or high blood pressure. Quitting smoking dramatically reduces the risk of heart disease and improves overall health.
4. Diabetes
Diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, significantly increases the risk of heart disease. When blood sugar levels are poorly controlled, they can damage the blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. People with diabetes are more likely to have high blood pressure and high cholesterol, both of which are contributing factors to heart disease. Proper diabetes management through diet, exercise, and medication can help reduce the risk of heart-related complications.
5. Obesity
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of heart disease in several ways. Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can contribute to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes—all risk factors for heart disease. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is crucial for protecting the heart. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly improve heart health.
6. Physical Inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle is a major contributor to heart disease. Regular physical activity helps to improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and maintain healthy cholesterol levels. Exercise also helps to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, along with strength training exercises twice a week.
7. Unhealthy Diet
An unhealthy diet, especially one high in saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and refined sugars, can increase your risk of heart disease. A poor diet contributes to high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes—all of which are risk factors for cardiovascular conditions. A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
8. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure, increase triglyceride levels, and lead to weight gain. Excessive alcohol consumption is also linked to an increased risk of arrhythmias and other heart-related issues. The American Heart Association recommends limiting alcohol intake to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men to maintain heart health.
9. Family History and Genetics
While most heart disease risk factors are controllable, genetics and family history play a role as well. If you have a family history of heart disease, you may be at a higher risk, particularly if your relatives developed heart disease at a young age. However, lifestyle choices still play a significant role in managing heart health, so even if you have a family history, you can reduce your risk through preventive measures.
10. Stress
Chronic stress can take a toll on the heart. Stress can increase blood pressure, contribute to unhealthy coping mechanisms like smoking or overeating, and exacerbate other risk factors for heart disease. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through relaxation techniques, exercise, or hobbies, is essential for protecting your heart.
How to Protect Your Heart
While certain risk factors are beyond your control, many of the factors that contribute to heart disease can be managed with the right lifestyle choices. Here are some key steps to help protect your heart:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (such as fish and legumes), and healthy fats (such as those from avocados and nuts). Limit your intake of processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats. Reducing sodium intake can also help manage blood pressure.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart, reduces blood pressure, and helps manage cholesterol and weight. Aim to incorporate both aerobic exercise (such as walking, cycling, or swimming) and strength training into your routine.
3. Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your heart. It can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease and improve your overall health. Seek support from healthcare professionals or support groups if needed.
4. Manage Stress
Practice stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress can help protect your heart and overall well-being.
5. Get Regular Health Check-ups
Regular health check-ups are crucial for monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels. Early detection of any abnormalities allows for prompt treatment and intervention.
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential for heart health. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can improve blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Conclusion
Heart disease is a complex condition influenced by various risk factors, but many of these factors are modifiable. By adopting heart-healthy habits such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing heart disease. It’s never too late to start protecting your heart—taking small steps today can lead to a healthier heart tomorrow. Keep an eye on your health, get regular check-ups, and make informed lifestyle choices to keep your heart strong for years to come.