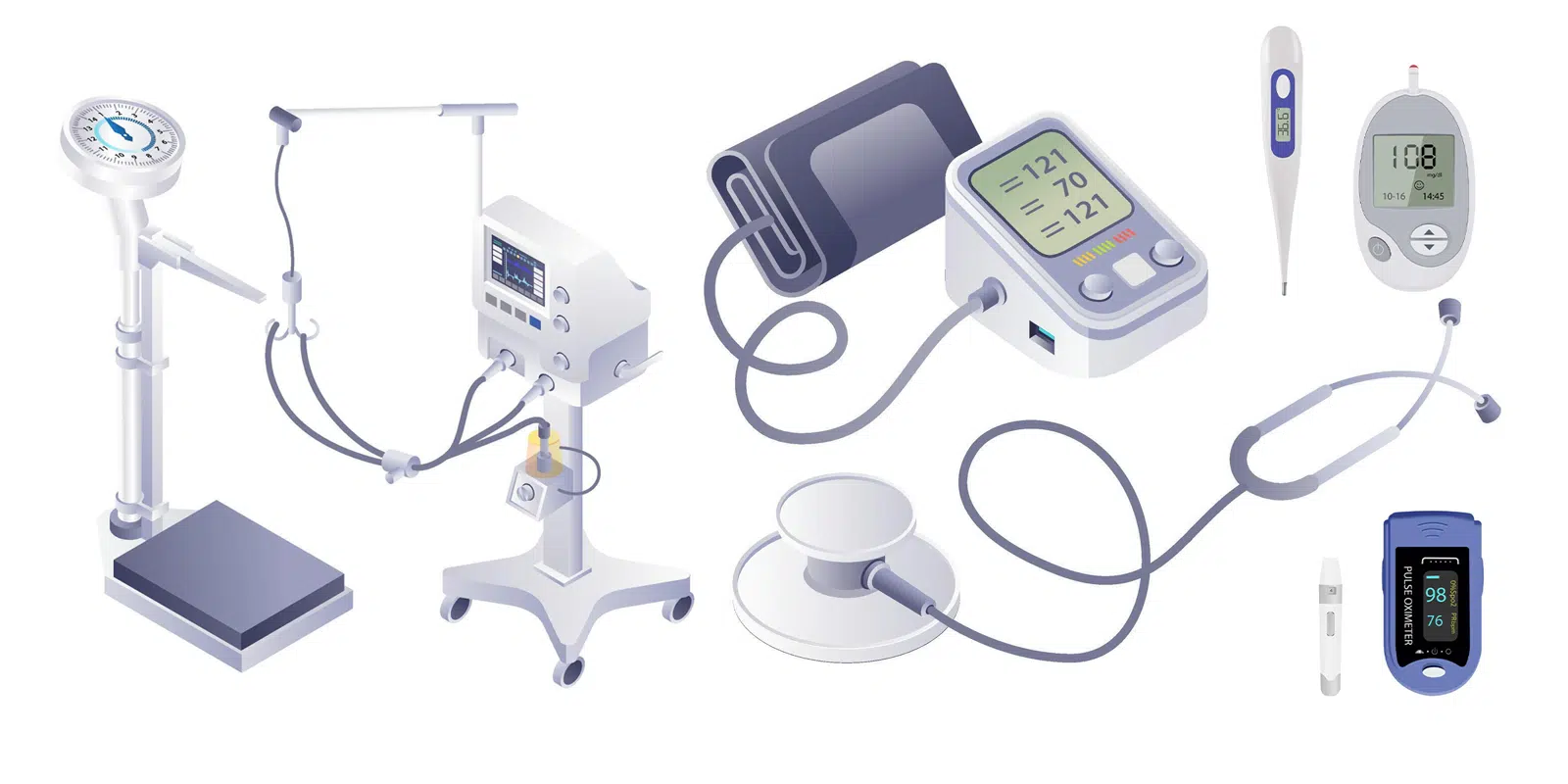
Types of Medical Devices Used in Hospitals – A Complete Guide!
Hospitals today are equipped with a wide range of medical devices that help doctors, nurses, and healthcare professionals diagnose, treat, and care for patients more efficiently. From simple tools like thermometers to complex machines like MRI scanners, these devices play a crucial role in modern healthcare.
In this article, we will explore the different types of medical devices used in hospitals, their purpose, and how they help save lives. Whether you’re a curious reader, a medical student, or someone working in the healthcare industry, this easy-to-understand guide will walk you through the essentials.
What Are Medical Devices?
Medical devices are tools, machines, implants, or instruments used to prevent, diagnose, monitor, or treat medical conditions. These devices vary widely in complexity—from basic tools like syringes to advanced machines like ventilators.
They are usually classified into three main categories based on their purpose and risk level:
- Class I – Low-risk (e.g., tongue depressors)
- Class II – Moderate-risk (e.g., infusion pumps)
- Class III – High-risk (e.g., pacemakers)
Major Types of Medical Devices Used in Hospitals
Let’s take a closer look at the main categories and examples of devices commonly found in hospitals.
1. Diagnostic Devices
These devices are used to identify or monitor a disease or condition. They help doctors detect problems early and plan the right treatment.
Examples:
- X-ray Machines – Used to see inside the body, especially bones and lungs.
- MRI Scanners – Create detailed images of organs, muscles, and tissues.
- CT Scanners – Combine X-rays and computer processing to give cross-sectional images.
- Ultrasound Machines – Use sound waves to create images of soft tissues and organs.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
Purpose: Early diagnosis, monitoring diseases, and guiding treatment.
2. Therapeutic Devices
These devices are used to treat or manage a medical condition, either by physical support or mechanical assistance.
Examples:
- Ventilators – Help patients breathe when they can’t do so on their own.
- Infusion Pumps – Deliver fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into the bloodstream.
- Dialysis Machines – Used for patients with kidney failure to clean their blood.
- Nebulizers – Turn liquid medicine into a mist to be inhaled into the lungs.
- Defibrillators – Deliver electric shocks to restore normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest.
Purpose: Support or replace bodily functions to help recovery.
3. Monitoring Devices
These devices are designed to track vital signs or body functions in real-time. They are essential for patients in ICU or those undergoing surgery.
Examples:
- Patient Monitors – Display heart rate, oxygen levels, blood pressure, and more.
- Pulse Oximeters – Measure the oxygen level in the blood.
- Glucose Monitors – Track blood sugar levels in diabetic patients.
- Fetal Monitors – Used during pregnancy to monitor the baby’s heartbeat and contractions.
Purpose: Continuous observation to ensure safety and respond to changes quickly.
4. Surgical Instruments and Tools
Hospitals require a wide range of manual tools and high-tech equipment for performing surgeries.
Examples:
- Scalpels and Forceps – Basic tools used for cutting and holding tissue.
- Endoscopes – Long, thin tubes with a camera used for viewing internal organs.
- Surgical Lasers – Used for precise cutting and removal of tissue.
- Electrosurgical Units – Use electrical current to cut tissue or stop bleeding.
- Anesthesia Machines – Deliver controlled amounts of anesthesia gases during surgery.
Purpose: Support safe and effective surgical procedures.
5. Hospital Beds and Mobility Aids
These may seem simple but are critical for patient comfort and mobility.
Examples:
- Adjustable Hospital Beds – Help patients sit up or lie down comfortably.
- Wheelchairs and Stretchers – For transporting patients within the hospital.
- Patient Lifts – Used to move patients safely from bed to chair or toilet.
Purpose: Improve patient comfort, reduce strain on caregivers, and prevent injury.
6. Sterilization and Disinfection Devices
These devices are essential for infection control, especially after surgeries or in ICU.
Examples:
- Autoclaves – Use steam to sterilize surgical instruments.
- UV Disinfection Systems – Use ultraviolet light to kill bacteria and viruses.
- Chemical Sterilizers – Use special solutions to clean sensitive equipment.
Purpose: Prevent infections and maintain a sterile environment.
7. Implants and Prosthetics
Some devices are used inside the body to replace or support body parts.
Examples:
- Pacemakers – Help control abnormal heart rhythms.
- Artificial Joints – Used in knee or hip replacement surgeries.
- Cochlear Implants – Help people with severe hearing loss.
- Stents – Open up blocked arteries in the heart.
Purpose: Long-term support or replacement of body functions.
Importance of Medical Devices in Hospitals
- Accurate Diagnosis: Devices help doctors detect issues early and start treatment faster.
- Effective Treatment: Many conditions that were once fatal are now treatable thanks to advanced equipment.
- Patient Safety: Monitoring devices help staff respond quickly to any changes in a patient’s condition.
- Improved Outcomes: Faster recovery, fewer complications, and better quality of care.
Challenges in Using Medical Devices
- High Cost: Advanced machines like MRI or robotic surgical systems are expensive.
- Training Needs: Staff must be well-trained to operate devices properly.
- Maintenance: Devices need regular maintenance and calibration for accuracy.
- Technology Changes: Hospitals must keep up with new innovations and upgrades.
Conclusion
Medical devices are the backbone of modern hospitals. They not only help in diagnosing and treating diseases but also improve patient comfort and safety. From life-saving machines like ventilators to simple tools like thermometers, each device plays a crucial role in the healthcare ecosystem.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more smart, connected, and efficient devices in the future—making healthcare safer and more effective for everyone.
FAQs About Medical Devices Used in Hospitals
1. What is the most commonly used medical device in hospitals?
The most commonly used devices include thermometers, blood pressure monitors, and patient monitors. These are used daily to check vital signs.
2. What device is used when a patient can’t breathe on their own?
A ventilator is used to help patients breathe when they are unable to do so naturally due to illness, surgery, or injury.
3. Are all medical devices high-tech?
No. While some devices like MRI machines are very advanced, others like syringes or bandages are very simple but still essential.
4. Who operates medical devices in hospitals?
Doctors, nurses, lab technicians, and biomedical engineers typically operate and maintain medical devices. Specialized training is often required.
5. How are medical devices maintained?
They are regularly cleaned, tested, and calibrated to ensure they work correctly. Hospitals usually have biomedical technicians for this task.