3 Strategies for Effective Weight Loss
Weight loss is the process of reducing total body mass by losing fluid, body fat, or lean mass, like bone and muscle. Individuals pursue this goal to improve health markers, enhance mobility, or change their appearance, but many struggle to achieve lasting results due to metabolic factors or lifestyle hurdles. While fad diets and trend-based exercise regimens often fail to produce sustainable outcomes, specific medical strategies can provide the structure necessary for success. Here is more information about three strategies for weight loss:
Understanding Weight Loss
Medical weight loss differs from self-directed diet plans because it is supervised by healthcare professionals who customize the program to your specific metabolic needs. A doctor or specialist evaluates your current health status, and then they create a plan that safely targets fat reduction while preserving muscle mass. This approach often integrates comprehensive lifestyle changes with medical interventions to support the body’s natural ability to shed excess pounds. Unlike commercial programs, professionals can help monitor underlying health conditions throughout the journey.
Implementing Dietary Modifications
A core component of any medical program involves structured dietary changes tailored to individual health requirements. Professionals might prescribe a low-calorie diet depending on the amount of weight a patient needs to lose. These plans emphasize nutrient-dense foods like lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains; they typically restrict processed sugars and unhealthy fats.
Some programs utilize meal replacements to simplify decision-making and control calorie intake. These options might include:
- High-protein shakes
- Nutrient-fortified bars
- Pre-packaged meals
By controlling portions and focusing on nutritional balance, patients can achieve a caloric deficit while still eating nutritious food. Registered dietitians often work alongside physicians to educate them on reading food labels, and they also offer information about planning meals. This education may help individuals to make healthier choices in the long-run.
Utilizing Prescription Medications
When diet and exercise alone do not yield the desired results, doctors may introduce prescription appetite suppressants. These medications work by altering brain chemistry to reduce feelings of hunger; they also increase feelings of fullness. By curbing cravings, these drugs may make it easier for patients to stick to their prescribed dietary plans without feeling constantly deprived.
Common types of FDA-approved weight management medications include:
- Semaglutide injections
- Tirzepatide
- Phentermine
Medications are most effective when used as part of a broader lifestyle intervention rather than a standalone solution. A healthcare provider will likely screen patients for potential side effects and contraindications before prescribing any drug. Regular check-ins allow the medical team to adjust dosages, and they can switch medications if a patient hits a plateau. This pharmacological support can be the catalyst needed to overcome biological barriers to weight reduction.
Increasing Physical Activity
Exercise is part of medical weight management, but the approach is often more gradual and personalized than typical gym memberships. AFter a provider assesses physical limitations, such as joint pain or cardiovascular issues, they can recommend safe and effective activities. The goal is to increase caloric expenditure and build lean muscle mass.
Patients might start with low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or stationary cycling. As fitness levels improve, the program may incorporate strength training exercises to further enhance metabolic rate. Physical activity also provides mental health benefits, reducing stress and anxiety that can lead to emotional eating. Consistency is key, so providers focus on finding activities that patients enjoy and can maintain long-term.
Learn More About Weight Loss
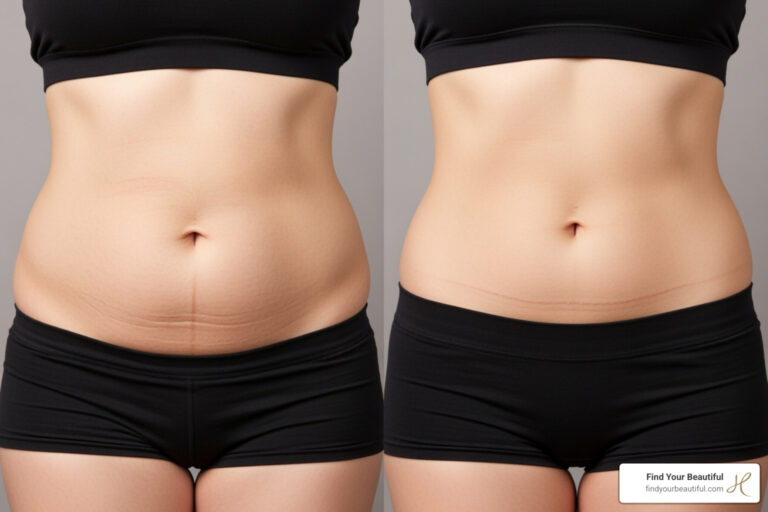
Effective weight management involves a multifaceted approach that addresses diet, biology, and lifestyle behaviors. Medical supervision offers a structured environment, and professionals guide you through dietary changes and appropriate medication use, as well as physical activity. To learn more about medical weight loss, consult a provider near you.